Which of the Following Is a Characteristic of Dispersion Forces
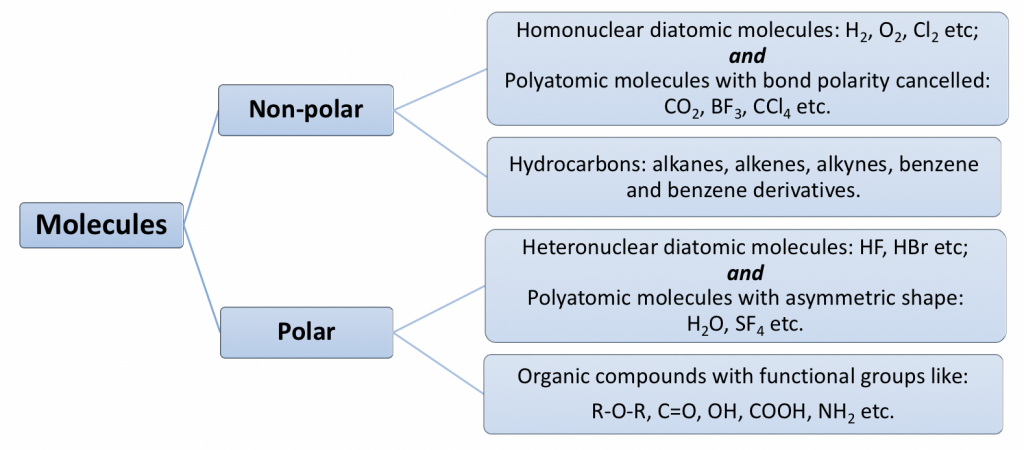
Dispersion forces are present in all molecules but non-polar molecules have only these forces. Molecular solids have relatively low melting points.
Bonding Practice Quiz 3 Chemistry Quiz Quizizz
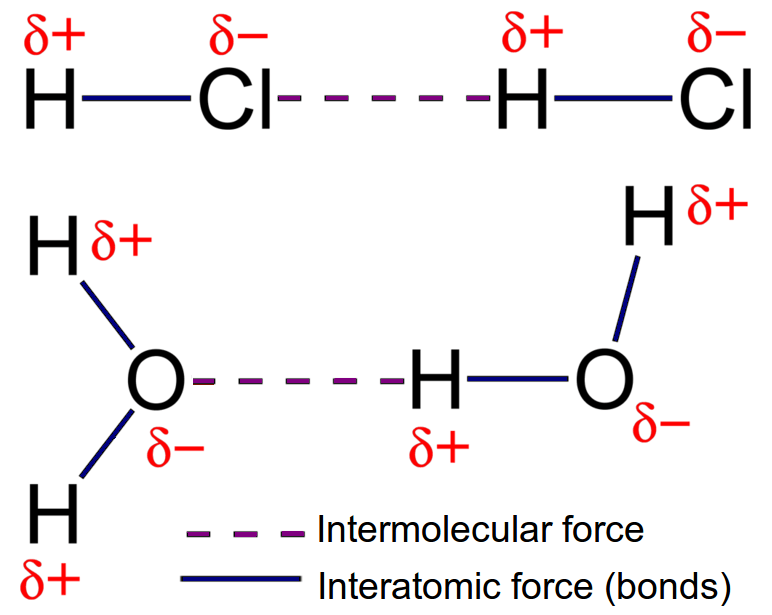
Molecules containing H bonded to F O or N.
. It is considered as the weakest of all intermolecular forces. Shape of the Molecule. A represents ion-dipole interactions and B represents hydrogen bonding.
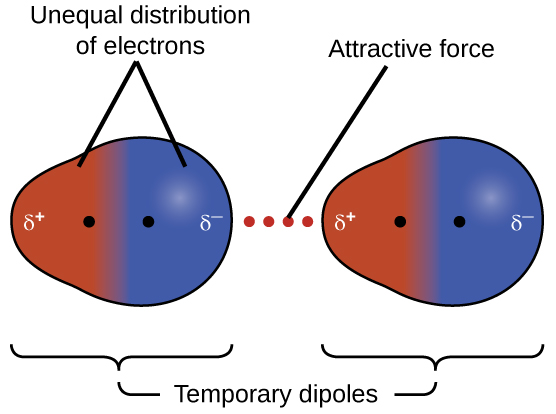
The electron cloud of the atoms are evenly distributed around the nucleus. Temporary dipoles can occur in non-polar molecules when the electrons that constantly orbit the nucleus occupy a similar location by chance. A Vanderwaal Force example of hydrogen bonds is the interaction of water molecules.
London dispersion forces tend to be. Tell whether each of the following is a characteristic of London dispersion forces LD dipole-dipole interactions di-di or hydrogen bonding HB. There is permanent - and ends that participate in electrostatic attractions c.
So this non polarity characteristics is produced due to the negligible negligible electronic activity difference. The lower boiling point of xenon can be explained by the stronger dispersion forces experienced by its atoms. Weaker between molecules that are not easily polarized.
London dispersion forces are intermolecular forces of attraction holding molecules together. 1 point A represents London dispersion forces and B represents hydrogen bonding. They are the weakest intermolecular force they increase as the molecular mass o a substance increases they form when a hydrogen atom interacts with an electronegative atom they are weaker than intramolecular bonds.
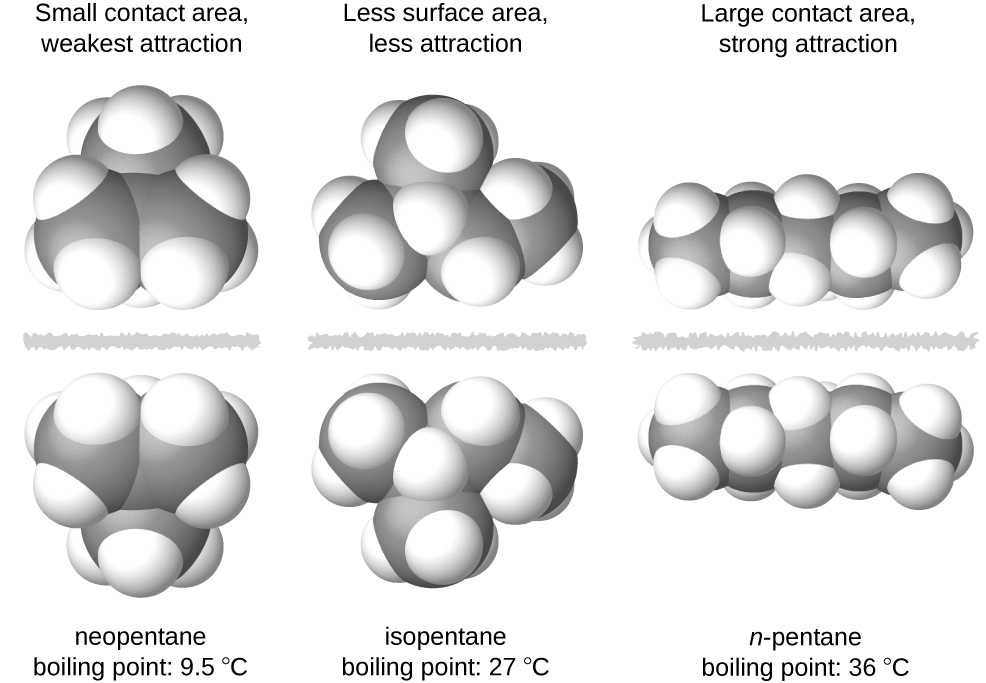
Which of the following conclusions about the two attractions is correct. Stronger in linear molecules than spherical molecules of similar molar mass. At room temperature neopentane C 5 H 12 is a gas whereas n-pentane C 5 H 12 is a liquid.
Dispersion forces that develop between atoms in different molecules can attract the two molecules to each other. Stronger between molecules that are easily polarized. The forces are relatively weak however and become significant only when the molecules are very close.
These bonds get stronger when they lie in a range of 04 kilojoules per mole kJmol and 4 kJmol. Which of the following characteristics indicates the presence of weak intermolecular forces in a liquid. Molecular Shape The shapes of molecules also affect the magnitudes of dispersion forces between them.
Dispersion forces are a basic force between two molecules or atoms but it is the weakest attractive force in between them called dispersion forces. The strength of Van Der Waal Dispersion forces increases with the size shape molar mass and number of electrons in an atom or a molecule. The electron cloud of the atoms is evenly distributed around nucleus.
Are found in only nonpolar substances. There is permanent - and ends that participate in electrostatic attractions c. I will have London dispersion forces.
Long unbranched molecules tend to feature stronger dispersion forces than branched short-chain molecules. Larger and heavier atoms and molecules exhibit stronger dispersion forces than do smaller and lighter atoms and molecules. London dispersion forces are weak intermolecular forces and are considered van der Waals forces.
In the following description the term particle will be used to refer to an atom molecule or ion. Musashixjubeio0 and 7 more users found this answer helpful. Argon molecule experiences dipolar characteristics when attracted by the hydrogen atom of HCl or repelled by the chlorine atom of HCl.
Mixtures of ionic compounds and polar compunds. There is instantaneous dipole that influences neighboring substances to gain dipoles b. The binding forces in molecular solids are dispersion forces or dispersion forces and dipole-dipole interactions.
Hence we can say that dispersion forces purely depend on the molecular. Components of These Forces. The type of inter molecular forces exist in and the component uh and they have characteristics non polarity.
Which of the following is a characteristic of dispersion forces. Stronger dispersion forces result in lower boiling points. As was the case for gaseous substances the kinetic molecular theory may be used to explain the behavior of solids and liquids.
_ the weakest intermolecular force the strongest intermolecular force the attraction between the positive end of one permanent dipole and the negative end of another the attraction between temporarily induced dipoles the. Since both are at room temperature they do not interact with each other. Molecular solids are usually excellent conductors of electric current.
Stronger in linear molecules than spherical molecules of similar molar mass. Which of the following is not characteristic of 1 point London Dispersion Forces. Are a type of permanent dipole.
There is instantaneous dipole that influences neighboring substances to gain dipoles b. They are the weakest of the intermolecular forces but become stronger as the size of the atoms in a molecule increases and they play a role in the physical characteristics of materials with heavy atoms. Ion-dipole hydrogen bonding dipole-dipole dispersion.
Van Der Waals dispersion forces are close-knit interactions depending on distance resulting in intermolecular attractions or repulsions. Polar molecules such as water create dipoles in neutral molecules like oxygen etc. Distinguishing characteristic of London dispersion forces a.
Which of the following is the characteristic of London dispersion forces. 5Distinguishing characteristic of London dispersion forces a. See the answer See the answer done loading.
There is permanent - and ends that participate in electrostatic attractions C. Dispersion forces ion-dipole and dipole-dipole E None. A a low heat of vaporization B a high boiling point.
A represents London dispersion forces and B represents ion-dipole interactions. Are found in only nonpolar substances. London dispersion forces LDF London dispersion forces are named after a German-American physicist Fritz London.
Rank the following types of intermolecular forces in general order of decreasing strength strongest to weakest. Are a type of permanent dipole. Stronger dispersion forces result in lower boiling points.
Dispersion forces occur in between the two atoms which have low molecular weight or two substances which are non-polar in type ie. The atoms of two neighbouring molecules participate in give and take of electrons. The electron cloud of the atoms are evenly distributed around the nucleus.
Note that we will use the popular phrase intermolecular attraction to refer to attractive forces between the particles of a substance regardless of.

Classify The Following Solids In Different Categories Based On The Nature Of Intermolecular Forces Operating In Them Potassium Sulphate Tin Benzene Urea Ammonia Water Zinc Sulphide Graphite Rubidium Argon Silicon Carbide
Intermolecular Forces Types Explanation Examples Psiberg
2 6 Intermolecular Force And Physical Properties Of Organic Compounds Organic Chemistry I
10 1 Intermolecular Forces Chemistry

Boiling Point And Melting Point In Organic Chemistry Chemistry Steps

10 1 Intermolecular Forces Chemistry

Intermolecular Forces Dipole And Induced Hydrogen Bond Videos Q A

London Dispersion Forces Definition Causes Examples

What Are 5 Characteristics Of Covalent Compounds Seniorcare2share
Difference Between Dipole Dipole And London Dispersion Forces Pediaa Com

Dispersion Force An Overview Sciencedirect Topics

1 Intermolecular Forces Liquids And Solids 2 Some Characteristic Properties Of The States Of Matter Gas Assumes Both The Volume And Shape Of The Container Ppt Download
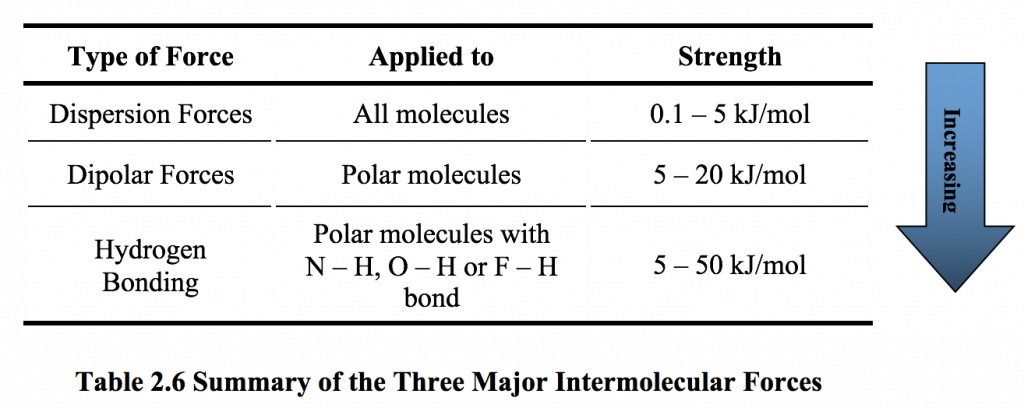
2 6 Intermolecular Force And Physical Properties Of Organic Compounds Organic Chemistry I
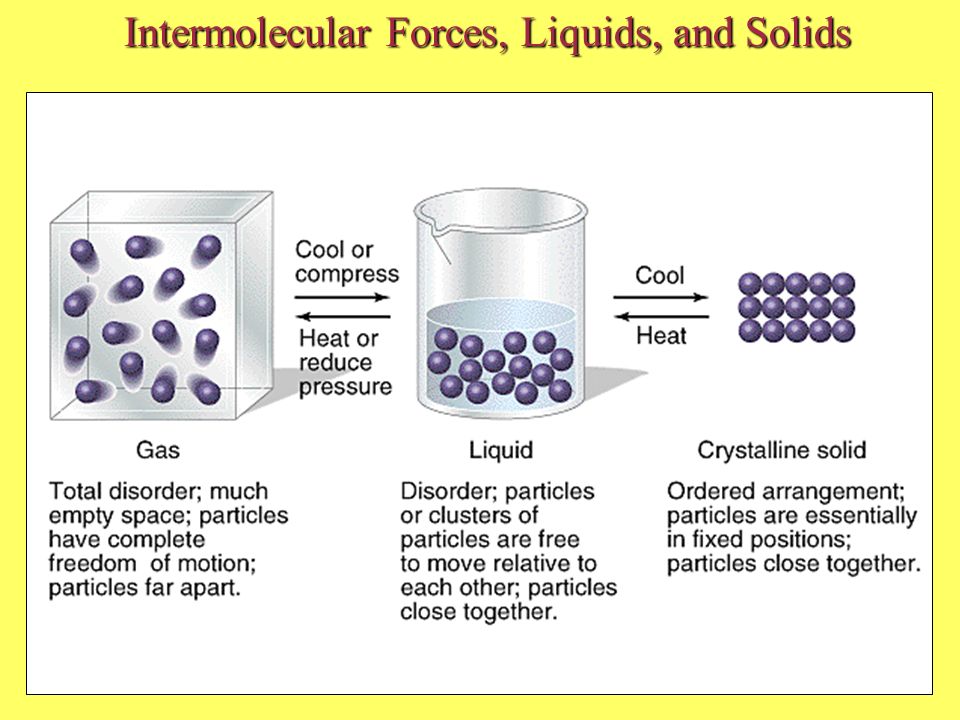
1 Intermolecular Forces Liquids And Solids 2 Some Characteristic Properties Of The States Of Matter Gas Assumes Both The Volume And Shape Of The Container Ppt Download

Intermolecular Forces Practice
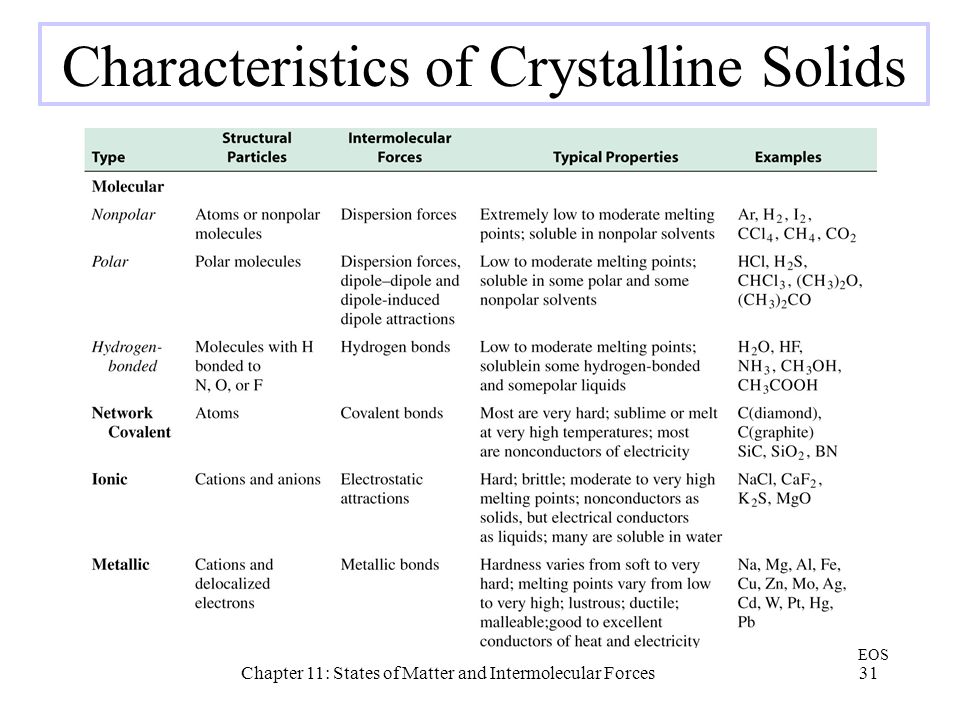
Chapter 11 States Of Matter And Intermolecular Forces Ppt Video Online Download

Solved Question 1 Evidence That Molecular Size Shape And Chegg Com

1 Intermolecular Forces Liquids And Solids 2 Some Characteristic Properties Of The States Of Matter Gas Assumes Both The Volume And Shape Of The Container Ppt Download
Comments
Post a Comment